Orally Disintegrating Tablets of Famotidine Prepared by Direct Compression Method Using 32 Full Factorial Design
Keywords:
Orally disintegrating tablets, Famotidine, Crospovidone, 3² full factorial designAbstract
Difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia) is common among all age groups, especially in elderly and pediatrics. Orally disintegrating tablets constitute an innovative dosage forms that overcome the problems of swallowing and provides a quick onset of action. The purpose of this study was to formulate and evaluate orally disintegrating tablet of
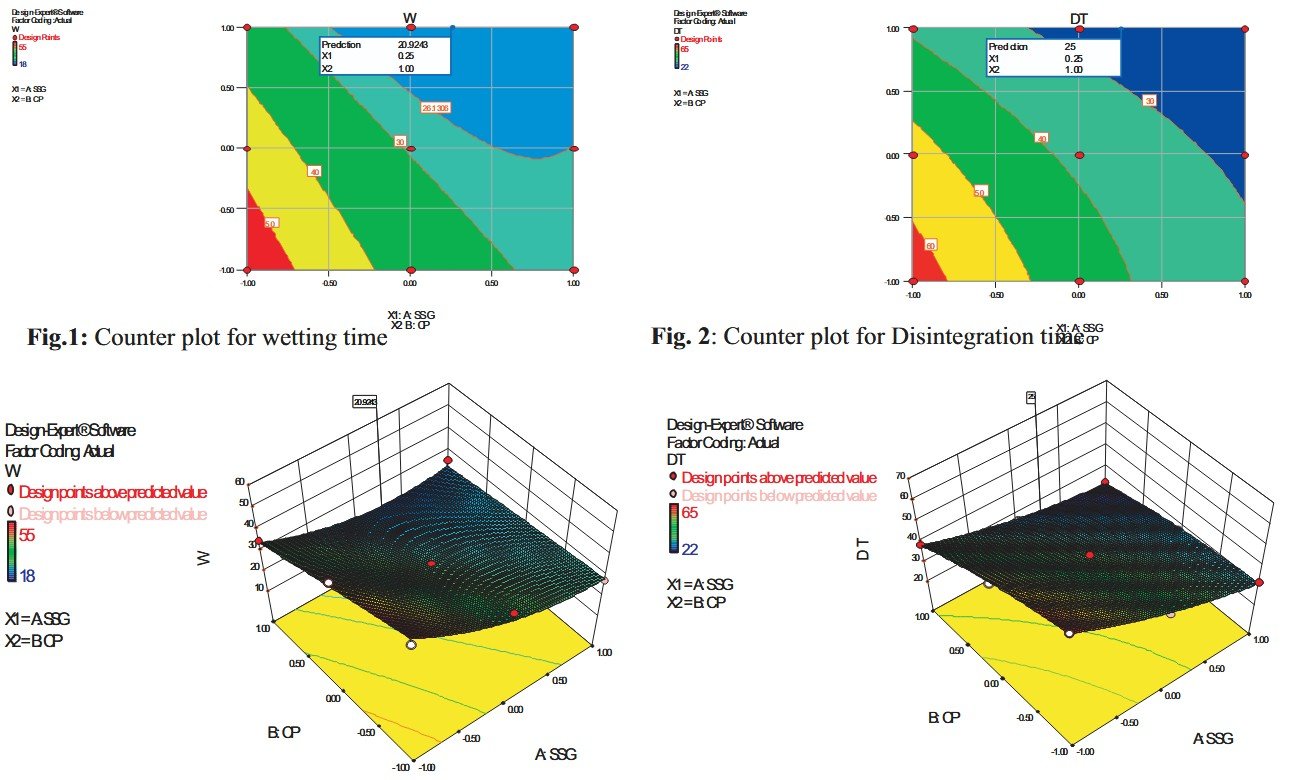
Famotidine using croscarmellose sodium and sodium starch glycolate (S.S.G.) as a superdisintegrant. Tablets were prepared by direct compression method. The Prepared tablets were evaluated for hardness, friability, thickness, drug content uniformity, in vitro dispersion time, wetting time and water absorption ratio. In the investigation, a 32 full factorial design was used to investigate the joint influence of 2 formulation variables: amount of S.S.G and Crospovidone. The results of multiple linear regression analysis revealed that for obtaining a rapidly disintegrating dosage form, tablets should be prepared using an optimum concentration of S.S.G and a higher percentage of Crospovidone. A contour plot is also presented to graphically represent the effect of the independent variables on the disintegration time and wetting time. A checkpoint batch was also prepared to prove the validity of the evolved mathematical model. The systematic formulation
approach helped in understanding the effect of formulation processing variables.