Comparison Of Susceptibility Test Methods For Determining Oxacillin Resistance In Clinical Isolates
Keywords:
PBP2a, MRSA, Laboratory diagnosis, Mec A geneAbstract
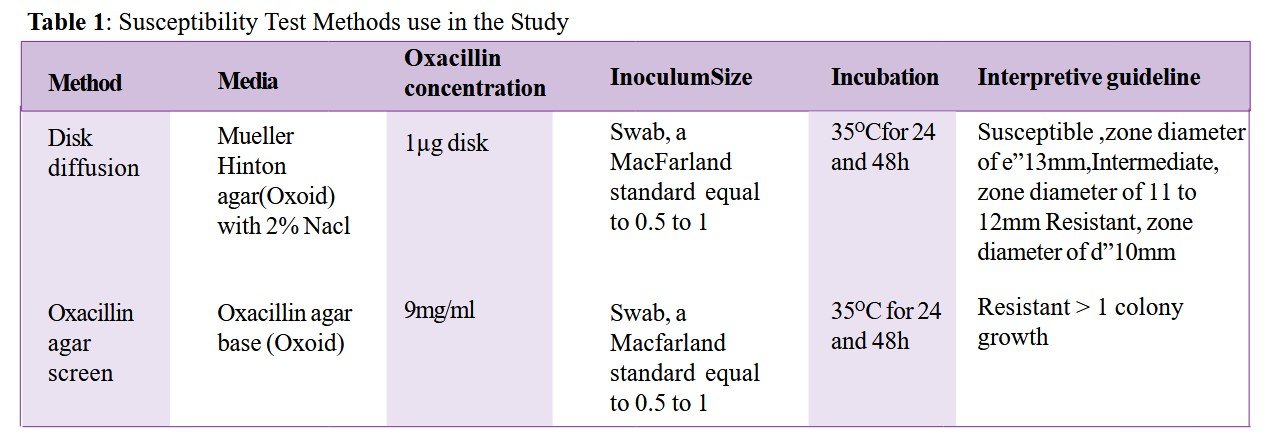
This study compared conventional phenotypic methods for detecting methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus with an established molecular method, using 30 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates from clinical specimens. Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion tests and oxacillin screen agar methods were performed, with the presence of penicillin-binding protein (PBP2a) as the reference standard. A commercial latex agglutination test (Oxoid, UK) was evaluated for detecting PBP2a, the MecA gene product. Of the 30 isolates, 20 were PBP2a-positive, with concomitant oxacillin resistance confirmed by Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion. All 30 isolates showed resistance via the disc diffusion method, achieving 100% sensitivity and specificity compared to PBP2a. The oxacillin agar screen method had 80% specificity and 73.3% sensitivity. While routine laboratory tests for MRSA detection showed variable specificity, MecA gene detection, the gold standard for confirming ambiguous results, is challenging in routine diagnostics. The Oxoid PBP2a detection kit offers a viable alternative for most laboratories.