A new improved RP-HPLC method for Assay of Bromelain, Trypsin, Rutoside and Diclofenac in bulk and Pharmaceutical Formulation
Keywords:
RP-HPLC, validation, stability studiesAbstract
Purpose: The present paper describes a simple, accurate and precise reversed phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) method for rapid and simultaneous quantification of Bromelain, Trypsin, Rutoside and Diclofenac.
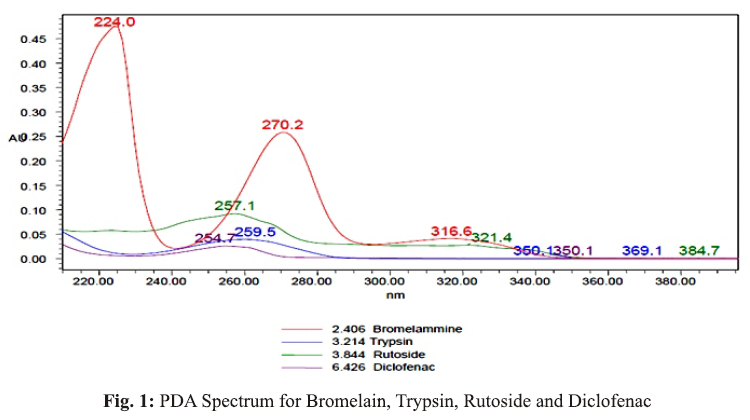
Method: The chromatographic separation was achieved on Inertsil ODS (250x4.6mm, 5µ). Mobile phase contained a mixture of OPA buffer at pH 2.4 and Acetonitrile in the ratio of 50:50 v/v, flow rate 1.0 ml/min and UV detection at 257nm.
Result: The proposed method shows a good linearity in the concentration range of 22.5-135 µg/ml for Bromelain, 12–72µg/ml of Trypsin, 25-150µg/ml of Rutoside and 12.5-75 µg/ml for Diclofenac under optimised conditions. Precision and recovery study results are in between 98-102%. In the entire robustness conditions %RSD is below 2.0%. Degradation has minimum effect in stress condition and solutions are stable up to 24 hrs.
Conclusion: This method is validated for different parameters like precision, linearity, accuracy, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), ruggedness, robustness and forced degradation study were determined according to the ICH Q2B guidelines. All the parameters of validation were found to be within the acceptance range of ICH guidelines.