Formulation Of Transdermal Drug Delivery System Of Metoprolol Tartrate And Its Evaluation
Keywords:
Metoprolol tartrate, Transdermal films, Invitro permeation studiesAbstract
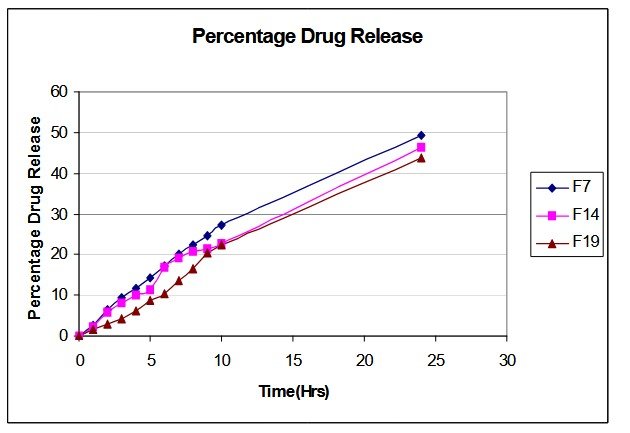
The oral bioavailability of Metoprolol tartrate is poor, prompting the formulation of matrix-type transdermal films to study the effect of polymers on drug release characteristics. The polymers used were cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB), polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP), ethyl cellulose (EC), and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC). Films were prepared using different polymer blends via the solvent casting method. Physicochemical evaluation of the polymer matrices was conducted to assess their suitability. Interactions among matrix components were analyzed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thin-layer chromatography. In-vitro permeation studies of optimized films, performed using a Franz diffusion cell, demonstrated steady-state and controlled drug release.