Development of some 1,2,3-triazole-based complexes incorporating hydroxy and acetamide groups: Synthesis, characterization, DFT calculation, and biological screening supported by molecular docking approach
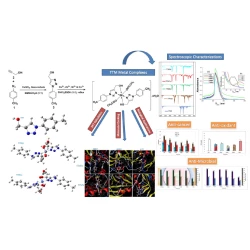
A versatile and effective ligand, 1-p-Tolyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol -4-yl-methanol (TTM) was been thoroughly characterized. Four novel coordination compounds derived from the TTM ligand were synthesized, and their structures were elucidated using a variety of spectroscopic and analytical techniques, including ultraviolet–visible (UV-Vis), infrared (IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (1H and 13C), and thermal analysis.
Keywords:
testAbstract
A versatile and effective ligand, 1-p-Tolyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol -4-yl-methanol (TTM) was been thoroughly characterized. Four novel coordination compounds derived from the TTM ligand were synthesized, and their structures were elucidated using a variety of spectroscopic and analytical techniques, including ultraviolet–visible (UV-Vis), infrared (IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (1H and 13C), and thermal analysis. In these complexes, metal coordination occurred via the nitrogen atom of the triazole ring and the terminal hydroxyl group. The thermal degradation behavior of the synthesized TTM complexes was investigated, revealing that they exhibit endothermic properties, as suggested by the calculated kinetic parameters for their various degradation stages. The structures proposed through density functional theory (DFT) calculations aligned well with the experimental findings, which confirmed the formation of complexes between the TTM and [Zn(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Co(II)] in a 2:1 ratio (L:M). In addition, the newly designed triazole-based complexes have an octahedral geometry, as evidenced by the correlation of the resulting analytical, chemical, and physical data. Antibacterial assays conducted against several bacterial and fungal strains demonstrated that the TTMCu complex displayed the highest activity, closely matching that of the reference standard. Additionally, the newly synthesized complexes were tested against various cell lines using the MTT assay, indicating potential anticancer properties as reflected in the percentage growth inhibition (IC50) values. Considering the IC50 values, the order of effectiveness was found as follows: TTM < TTMCo < TTMZn < TTMNi < TTMCu, across the MCF-7 (breast cancer), Hep-G2 (hepatocellular carcinoma), and HCT-116 (colon cancer) cell lines. Such activity emphasizes their potential as anticancer agents. Promising results were further supported by pharmacophore modeling and Swiss-ADME calculations. The in silico data highlighted a significant enhancement in activity upon complexation with metal ions, contrasting with the lower activity observed for the free ligand, which aligns with the experimental results. Our findings revealed that triazole-based copper complex (TTMCu) could be employed as a promising antimicrobial and anticancer drug.