Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of the peel extract of Psidium Guajava Fruit on selected bacterial strains
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ajphs.2023.13.39Keywords:
Guava peel, Phytochemical constituents, Antimicrobial activity, E. coli and S. aureusAbstract
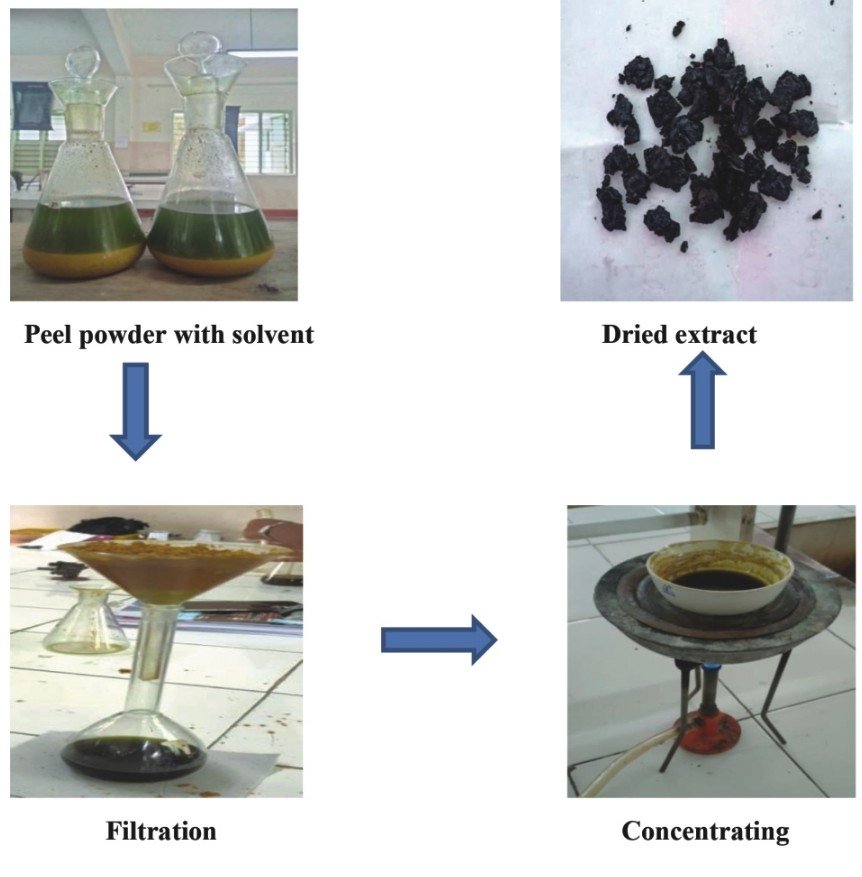
Plants and plants extracts have important role in modern medicine as their chemical and medical constituents are found in natural form. Plants and plant based products are bases of many modern pharmaceuticals that are currently in use for various diseases. Psidium guajava is an Indian medicinal plant belongs to the family Myrtaceae. The present study has been designed to screen the pharmacological studies such as antimicrobial activity of fruit peels of psidium guajava extracts on bacterial strains (E. coli and S. aureus). The ethanol extract of P. guajava fruit peel has demonstrated promising antimicrobial properties. Increasing awareness, promotion and utilization of this fruit for public benefits are highly encouraged and identification of active phytoconstiuents in the extracts will serve as a natural cytotoxic agent against various cancers.