The clinical pharmacology of milk-drug interactions: from pharmacokinetic principles to recent therapeutic recommendations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ajphs.2025.15.91Keywords:
Drug-food interactions, Milk, Pharmacokinetics, Chelation, Therapeutic efficacyAbstract
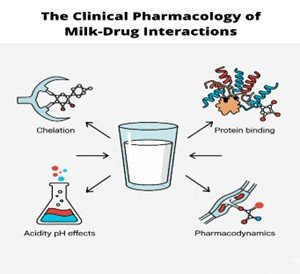
Milk consumption can significantly alter the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of drugs, impacting their therapeutic efficacy and safety. These interactions primarily affect orally administered medications through several key mechanisms. This review aims to systematically summarize the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic mechanisms of milk-drug interactions, analyze their clinical implications across diverse populations, and provide practical recommendations to optimize therapeutic efficacy and safety. A major factor is milk's high calcium content, which can chelate with drugs like tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones, forming insoluble complexes that may reduce drug bioavailability by as much as 50–60%. Furthermore, milk proteins such as casein can bind to medications, altering their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. The fat content in milk plays a dual role, enhancing the absorption of lipophilic drugs like griseofulvin while potentially delaying the absorption of hydrophilic drugs. Milk also acts as a buffer, raising gastric pH and thereby impairing the dissolution of acid-dependent drugs. While most interactions are pharmacokinetic, some pharmacodynamic effects are notable, such as the risk of a hypertensive crisis when patients on monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) consume tyramine-rich aged cheeses. The clinical implications are significant, especially for vulnerable populations like children and the elderly who frequently consume milk and take medications. To avoid therapeutic failure or toxicity, healthcare providers should offer personalized dietary advice. A common recommendation is to separate drug administration from milk consumption by at least one to two hours to ensure optimal medication effectiveness and safety.
References
Aalaei, K., Khakimov, B., De Gobba, C., & Ahrné, L. (2021). Gastric digestion of milk proteins in adult and elderly: Effect of high-pressure processing. Foods, 10(4), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040786
Abuhelwa, A., Williams, D., Upton, R., & Foster, D. (2017). Food, gastrointestinal pH, and models of oral drug absorption. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 112, 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.11.034
Al-Behaisi, S., Antal, I., Morovján, G., Drabant, S., Plachy, J., Marton, S., & Klebovich, I. (2002). Study of the acid buffering capacity of dietary components regarding food-drug interactions. Acta Pharmaceutica Hungarica, 72(3), 151–157. PMID: 12494789.
Auestad, N., & Layman, D. (2021). Dairy bioactive proteins and peptides: a narrative review. Nutrition Reviews, 79(Suppl 1), 60–68. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuab097
Austin, J., Klein, K., Mattek, N., & Kaye, J. (2017). Variability in medication taking is associated with cognitive performance in nondemented older adults. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring, 6, 124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dadm.2017.02.003
Berry, M. (2004). Mammalian central nervous system trace amines. Pharmacologic amphetamines, physiologic neuromodulators. Journal of Neurochemistry, 90(2), 257–271. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02501.x
Boyd, B., Salim, M., Clulow, A., Ramirez, G., Pham, A., & Hawley, A. (2018). The impact of digestion is essential to the understanding of milk as a drug delivery system for poorly water soluble drugs. Journal of Controlled Release, 292, 13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.10.027
Charkoftaki, G., Kytariolos, J., & Macheras, P. (2010). Novel milk-based oral formulations: proof of concept. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 390(2), 176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.01.038
Chen, M., Zhou, S., Fabriaga, E., Zhang, P., & Zhou, Q. (2018). Food-drug interactions precipitated by fruit juices other than grapefruit juice: An update review. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 26(2), S61–S71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2018.01.009
Cho, M., Shin, D., Chang, S., Lee, J., Jeong, S., Kim, S., Yun, J., & Son, K. (2018). Association between cognitive impairment and poor antihypertensive medication adherence in elderly hypertensive patients without dementia. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 10834. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29974-7
Chon, D., Reisman, T., Weinreb, J., Hershman, J., & Leung, A. (2018). Concurrent milk ingestion decreases absorption of levothyroxine. Thyroid, 28(4), 454–457. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2017.0428
Cooper, K., Martin, P., Dane, A., Warwick, M., Raza, A., & Schneck, D. (2003). Lack of effect of ketoconazole on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in healthy subjects. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 55(1), 94–99. https://doi.org/10.1046/J.1365-2125.2003.01720.X
D'andrea, G., Terrazzino, S., Fortin, D., Farruggio, A., Rinaldi, L., & Leon, A. (2003). HPLC electrochemical detection of trace amines in human plasma and platelets and expression of mRNA transcripts of trace amine receptors in circulating leukocytes. Neuroscience Letters, 346(1-2), 89–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(03)00573-1
Dhore, P., Dave, V., Saoji, S., Bobde, Y., Mack, C., & Raut, N. (2017). Enhancement of the aqueous solubility and permeability of a poorly water soluble drug ritonavir via lyophilized milk-based solid dispersions. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 22(4), 536–546. https://doi.org/10.1080/10837450.2016.1193193
Eljaaly, K., Helal, A., Almandeel, T., Algarni, R., & Alshehri, S. (2021). Multivalent cations interactions with fluoroquinolones or tetracyclines: A cross-sectional study. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(10), 5824–5829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.07.065
Gainetdinov, R., Hoener, M., & Berry, M. (2018). Trace amines and their receptors. Pharmacological Reviews, 70(3), 549–620. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.117.015305
Gertz, B., Holland, S., Kline, W., Matuszewski, B., Freeman, A., Quan, H., Lasseter, K., Mucklow, J., & Porras, A. (1995). Studies of the oral bioavailability of alendronate. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 58(3), 288–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-9236(95)90245-7
Gil, Á., & Ortega, R. (2009). Introduction and executive summary of the supplement, role of milk and dairy products in health and prevention of noncommunicable chronic diseases: A series of systematic reviews. Advances in Nutrition, 10(suppl_2), S67–S73. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmz020
Gillman, P. (2018). A reassessment of the safety profile of monoamine oxidase inhibitors: elucidating tired old tyramine myths. Journal of Neural Transmission, 125(11), 1707–1725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1932-y
Hallberg, L., Rossander-Hultén, L., Brune, M., & Gleerup, A. (1992). Calcium and iron absorption: mechanism of action and nutritional importance. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 46(5), 317–327.
Huang, D., Wu, Q., Xu, X., Ji, C., Xia, Y., Zhao, Z., Dai, H., Li, H., Gao, S., Chang, Q., & Zhao, Y. (2022). Maternal consumption of milk or dairy products during pregnancy and birth outcomes: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9, 900529. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.900529
Ichikawa, R., Shibata, M., Nakura, Y., Iizuka, K., Uenishi, K., Sekiya, T., Suzuki, A., & Nishizawa, H. (2025). Inadequate calcium and vitamin D intake among Japanese women during the perinatal period: A cross-sectional study with bone health assessment. Nutrients, 17(6), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061075
Khan, I., Nadeem, M., Imran, M., Asif, M., Khan, M., Din, A., & Ullah, R. (2019). Triglyceride, fatty acid profile and antioxidant characteristics of low melting point fractions of Buffalo Milk fat. Lipids in Health and Disease, 18(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-019-0995-6
Kim, M., Oh, S., & Imm, J. (2018). Buffering capacity of dairy powders and their effect on yoghurt quality. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources, 38(2), 273–282. https://doi.org/10.5851/kosfa.2018.38.2.273
Koziolek, M., Alcaro, S., Augustijns, P., Basit, A., Grimm, M., Hens, B., Hoad, C., Jedamzik, P., Madla, C., Maliepaard, M., Marciani, L., Maruca, A., Parrott, N., Pávek, P., Porter, C., Reppas, C., Van Riet-Nales, D., Rubbens, J., Statelova, M., Trevaskis, N., Valentová, K., Vertzoni, M., Čepo, D., & Corsetti, M. (2019). The mechanisms of pharmacokinetic food-drug interactions - A perspective from the UNGAP group. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 134, 31–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2019.04.003
Krishnan, K. (2007). Revisiting monoamine oxidase inhibitors. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 68(Suppl 8), 35–41.
Kruger, H., Rautenbach, P., Venter, C., Wright, H., & Schwarz, P. (2007). An inverse association between calcium and adiposity in women with high fat and calcium intakes. Ethnicity & Disease, 17(1), 93–98.
Lambrini, K., Aikaterini, F., Konstantinos, K., Christos, I., Ioanna, P., & Areti, T. (2021). Milk nutritional composition and its role in human health. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 9(1), 10–15. https://doi.org/10.17265/2328-2150/2021.01.002
Lee, J., Kwak, H., Shin, D., Seo, H., Park, S., Hong, B., Shin, M., Kim, S., & Kang, K. (2022). Mitigation of gastric damage using Cinnamomum cassia extract: Network pharmacological analysis of active compounds and protection effects in rats. Plants, 11(6), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11060716
Lehto, P., & Kivistö, K. (1995). Effects of milk and food on the absorption of enoxacin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 39(2), 194–196. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1365-2125.1995.TB04431.X
Leyden, J. (1985). Absorption of minocycline hydrochloride and tetracycline hydrochloride. Effect of food, milk, and iron. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 12(2 Pt 1), 308–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(85)80041-4
Liu, H., Lu, M., Hu, J., Fu, G., Feng, Q., Sun, S., & Chen, C. (2023). Medications and food interfering with the bioavailability of levothyroxine: A systematic review. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 19, 593–606. https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S414460
Lynch, S. (2000). The effect of calcium on iron absorption. Nutrition Research Reviews, 13(2), 141–158. https://doi.org/10.1079/095442200108729043
Macheras, P., Koupparis, M., & Antimisiaris, S. (1989). Effect of temperature and fat content on the solubility of hydrochlorothiazide and chlorothiazide in milk. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 78(11), 942–944.
Martínez, J., Escudero, E., Badillo, E., Yuste, M., Galecio, J., & Marín, P. (2024). Pharmacokinetics of doxycycline in plasma and milk after intravenous and intramuscular administration in dairy goats. Animals, 14(16), 2416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162416
Matar, C., Amiot, J., Savoie, L., & Goulet, J. (1996). The effect of milk fermentation by Lactobacillus helveticus on the release of peptides during in vitro digestion. Journal of Dairy Science, 79(6), 971–979. https://doi.org/10.3168/JDS.S0022-0302(96)76448-2
Medarov, B. (2009). Milk-alkali syndrome. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 84(3), 261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-6196(11)61144-0
Misselwitz, B., Butter, M., Verbeke, K., & Fox, M. (2019). Update on lactose malabsorption and intolerance: pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management. Gut, 68(11), 2080–2091. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318404
Mitchell, D., Heise, M., Pallone, K., Clay, M., Nesbitt, J., Russell, D., & Melson, C. (1999). The effect of dosing regimen on the pharmacokinetics of risedronate. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 48(4), 536–542. https://doi.org/10.1046/J.1365-2125.1999.00035.X
Neuvonen, P. (1976). Interactions with the absorption of tetracyclines. Drugs, 11(1), 45–54. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-197611010-00004
Neuvonen, P., Kivistö, K., & Lehto, P. (1991). Interference of dairy products with the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 50(5 Pt 1), 498–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.1991.174
Nicolas, J., Bouzom, F., Hugues, C., & Ungell, A. (2017). Oral drug absorption in pediatrics: the intestinal wall, its developmental changes and current tools for predictions. Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition, 38(2), 83–106. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.2052
Ogawa, R., & Echizen, H. (2010). Drug-drug interaction profiles of proton pump inhibitors. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 49(8), 509–533. https://doi.org/10.2165/11531320-000000000-00000
Pandey, P., & Kumar, S. (2022). Influence of interaction of milk fat on release, characteristics and absorption of theophylline. Indian Drugs, 59(01), 21–29. https://doi.org/10.53879/id.59.01.12239
Pápai, K., Budai, M., Ludányi, K., Antal, I., & Klebovich, I. (2010). In vitro food-drug interaction study: Which milk component has a decreasing effect on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin? Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 52(1), 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2009.12.003
Pavlović, N., Goločorbin-Kon, S., Ðanić, M., Stanimirov, B., Al‐Salami, H., Stankov, K., & Mikov, M. (2018). Bile acids and their derivatives as potential modifiers of drug release and pharmacokinetic profiles. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01283
Podany, A., Scarsi, K., & Fletcher, C. (2016). Comparative clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitors. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 56(1), 25–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-016-0424-1
Ponsonby-Thomas, E., Pham, A., Huang, S., Salim, M., Klein, L., Offersen, S., Thymann, T., & Boyd, B. (2024). Human milk improves the oral bioavailability of the poorly water-soluble drug clofazimine. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 197, 114604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114604
Pressler, R., Abend, N., Auvin, S., Boylan, G., Brigo, F., Cilio, M., De Vries, L., Elia, M., Espeche, A., Hahn, C., Inder, T., Jette, N., Kakooza-Mwesige, A., Mader, S., Mizrahi, E., Moshé, S., Nagarajan, L., Noyman, I., Nunes, M., Samia, P., Shany, E., Shellhaas, R., Subota, A., Triki, C., Tsuchida, T., Vinayan, K., Wilmshurst, J., Yozawitz, E., & Hartmann, H. (2023). Treatment of seizures in the neonate: Guidelines and consensus‐based recommendations—Special report from the ILAE Task Force on Neonatal Seizures. Epilepsia, 64(10), 2555–2570. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.17745
Reis, A., & Joaquim, J. (2015). Drug interaction with milk and the relevance of acidifying/alkalizing nature of food. Clinical Therapeutics, 37(8), e109. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLINTHERA.2015.05.202
Ruiz-Hurtado, P., Garduño‐Siciliano, L., Domínguez-Verano, P., Balderas-Cordero, D., Gorgua-Jiménez, G., Canales-Alvarez, O., Canales-Martínez, M., & Rodríguez-Monroy, M. (2021). Propolis and its gastroprotective effects on NSAID-induced gastric ulcer disease: A systematic review. Nutrients, 13(9), 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093169
Ruiz-Ramos, J., Gras-Martín, L., & Ramírez, P. (2023). Antimicrobial pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in critical care: Adjusting the dose in extracorporeal circulation and to prevent the genesis of multiresistant bacteria. Antibiotics, 12(3), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030475
Salter, M., & Kenney, A. (2018). Myocardial injury from tranylcypromine-induced hypertensive crisis secondary to excessive tyramine intake. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 18(6), 578–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-018-9476-9
Sanka, K., Munjulury, V., Mohd, A., & Diwan, P. (2014). Enhancement of solubility, dissolution release profile and reduction in ulcerogenicity of piroxicam by inclusion complex with skimmed milk. Drug Delivery, 21(4), 295–303. https://doi.org/10.3109/10717544.2013.856964
Sinawe, H., & Casadesus, D. (2023). Ketoconazole. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559221/
Smith, D., Lovell, J., Weller, C., Kennedy, B., Winbolt, M., Young, C., & Ibrahim, J. (2017). A systematic review of medication non-adherence in persons with dementia or cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE, 12(2), e0170651. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170651
Sonar, P., Behera, A., Banerjee, S., Gaikwad, D., & Harer, S. (2015). Preparation and characterization of simvastatin solid dispersion using skimmed milk. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 41(7), 1153–1163. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2013.845836
Song, I., Borland, J., Arya, N., Wynne, B., & Piscitelli, S. (2014). Pharmacokinetics of dolutegravir when administered with mineral supplements in healthy adult subjects. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 55(5), 490–496. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.439
Song, I., Borland, J., Chen, S., Patel, P., Wajima, T., Peppercorn, A., & Piscitelli, S. (2011). Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of the integrase inhibitor dolutegravir. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 56(3), 1627–1629. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.05739-11
Stacher, G., Granser, G., Bergmann, H., Kugi, A., Stacher-Janotta, G., & Höbart, J. (1991). Slow gastric emptying induced by high fat content of meal accelerated by cisapride administered rectally. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 36(11), 1621–1627. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01307519
Steardo, L., Luciano, M., Sampogna, G., Carbone, E., Caivano, V., Di Cerbo, A., Giallonardo, V., Palummo, C., Vece, A., Del Vecchio, V., De Fazio, P., & Fiorillo, A. (2020). Clinical severity and calcium metabolism in patients with bipolar disorder. Brain Sciences, 10(7), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10070417
Subkisha, M., Immaculate, J., Janani, B., & Lavanya, E. (2024). Antibiotics interaction with dairy products - Exploring health impacts and treatment consideration. Journal for Research in Applied Sciences and Biotechnology, 3(4), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.55544/jrasb.3.4.1
Tao, R., Prajapati, S., Pixley, J., Grada, A., & Feldman, S. (2023). Oral tetracycline-class drugs in dermatology: Impact of food intake on absorption and efficacy. Antibiotics, 12(7), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12071152
Thyroid disease in pregnancy: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 223. (2020). Obstetrics and Gynecology, 135(6), e261–e274. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000003893
Varounis, C., Katsi, V., Nihoyannopoulos, P., Lekakis, J., & Tousoulis, D. (2017). Cardiovascular hypertensive crisis: Recent evidence and review of the literature. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 3, 51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2016.00051
Vegarud, G., Langsrud, T., & Svenning, C. (2000). Mineral-binding milk proteins and peptides; occurrence, biochemical and technological characteristics. British Journal of Nutrition, 84(S1), S91-S98. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114500002300
Virili, C., Giovanella, L., Fallahi, P., Antonelli, A., Santaguida, M., Centanni, M., & Trimboli, P. (2018). Levothyroxine therapy: Changes of TSH levels by switching patients from tablet to liquid formulation. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 9, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00010
Walden, D., Khotimchenko, M., Hou, H., Chakravarty, K., & Varshney, J. (2021). Effects of magnesium, calcium, and aluminum chelation on fluoroquinolone absorption rate and bioavailability: A computational study. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050594
Walters, K., Myers, K., Ingle, A., Donohue, T., & Noguera, D. (2024). Effect of temperature and pH on microbial communities fermenting a dairy coproduct mixture. Fermentation, 10(8), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080422
Waters, L., Winston, A., Reeves, I., Boffito, M., Churchill, D., Cromarty, B., Dunn, D., Fink, D., Fidler, S., Foster, C., Fox, J., Gupta, R., Hilton, A., Khoo, S., Leen, C., Mackie, N., Naous, N., Ogbonmwan, D., Orkin, C., Panton, L., Post, F., Pozniak, A., Sabin, C., & Walsh, J. (2022). BHIVA guidelines on antiretroviral treatment for adults living with HIV‐1 2022. HIV Medicine, 23(S5), 3–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/hiv.13446
Wiesner, A., Gajewska, D., & Paśko, P. (2021). Levothyroxine interactions with food and dietary supplements–A systematic review. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030206
Wiesner, A., Zagrodzki, P., Gawalska, A., & Paśko, P. (2024b). Together or apart? Revealing the impact of dietary interventions on bioavailability of quinolones: A systematic review with meta-analyses. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 63(6), 617–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-024-01377-0
Wiesner, A., Zagrodzki, P., Gawalska, A., & Paśko, P. (2024c). Clinically important interactions of macrolides and tetracyclines with dietary interventions—a systematic review with meta-analyses. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 79(10), dkae315. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkae315
Wiesner, A., Zagrodzki, P., & Paśko, P. (2024a). Do dietary interventions exert clinically important effects on the bioavailability of β-lactam antibiotics? A systematic review with meta-analyses. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 79(3), 565–577. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkae028
Wilkins Parker, L. R., & Preuss, C. V. (2023). Alendronate. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526073/
Xue, H., Zhang, M., Ma, J., Chen, T., Wang, F., & Tang, X. (2020). Lactose-induced chronic diarrhea results from abnormal luminal microbial fermentation and disorder of ion transport in the colon. Frontiers in Physiology, 11, 877. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00877
Zamfirescu, I., & Carlson, H. (2011). Absorption of levothyroxine when coadministered with various calcium formulations. Thyroid, 21(5), 483–486. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2010.0296
Zergiebel, S., Ueberschaar, N., & Seeling, A. (2022). Development and optimization of an ultra-fast microextraction followed by HPLC-UV of tetracycline residues in milk products. Food Chemistry, 402, 134270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134270
Zielińska, M., Garbacz, G., Sczodrok, J., & Voelkel, A. (2022). The effects of various food products on bisphosphonate’s availability. Pharmaceutics, 14(4), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040717