Ethosome as a colloidal carrier for nasal drug delivery for brain targeting: a review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/ajphs.2025.15.80Keywords:
Ethosome, Ethanol, Composition of ethosome, Drug absorption through noseAbstract
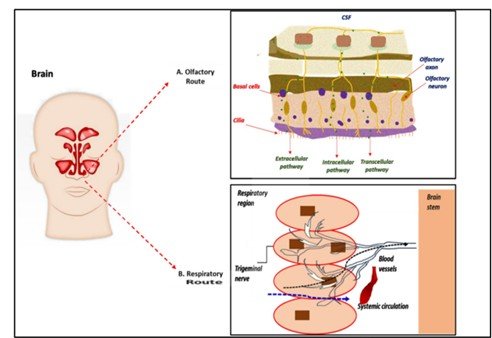
As a non-invasive method that offers quick absorption, avoids hepatic first-pass metabolism, and promotes patient compliance, nasal medication delivery has garnered increasing interest. However, its efficacy is hampered by issues including mucociliary clearance and the restricted permeability of big or hydrophilic compounds. A possible remedy is offered by ethosomes, which are new phospholipid-based vesicular carriers enhanced with ethanol that improve drug solubility, stability, and penetration through the nasal mucosa. Their special deformable structure protects against enzymatic degradation and enables better trapping of a variety of medicinal substances, including small molecules, peptides, and proteins. Recent investigations have highlighted their potential to increase bioavailability, prolong drug release, and achieve targeted nasal delivery. Ethosomes, flexible lipid-based vesicular carriers enriched with ethanol, represent a novel strategy for enhancing drug absorption through the nasal mucosa. Their high deformability allows them to penetrate efficiently through both transcellular and paracellular pathways, while ethanol acts as a permeation enhancer by fluidizing epithelial membranes and opening tight junctions. Ethosomes also protect labile drugs such as peptides and proteins from enzymatic degradation and support sustained release, making them particularly valuable for brain targeting via the nasal route. This unique combination of flexibility, enhanced permeability, and protective capability positions ethosomes as an innovative and promising platform for improving nasal drug delivery and overcoming the limitations of conventional formulations.
References
Aute, P. P., Kamble, M. S., Chaudhari, P. D., & Bhosale, A. V. (2012). A comprehensive review on ethosomes. International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy & Life Sciences, 2(1), 218–224.
Bilapatte, A., More, A., Satpute, K., & Syed, S. M. (2025). Formulation and evaluation of carbamazepine-loaded ethosomal nasal in-situ gel for brain-targeted drug delivery. Journal of Holistic Integrative Pharmacy, 6(1), 57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhip.2025.03.002
Celia, C., Trapasso, E., Cosco, D., Paolino, D., & Fresta, M. (2009). Turbiscan Lab® Expert analysis of the stability of ethosomes® and ultradeformable liposomes containing a bilayer fluidizing agent. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 72(1), 155–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.03.007
Desai, G. N., Dandagi, P. M., & Kazi, T. M. (2023). Nanosized intranasal delivery of novel self-assembled cubic liquid crystals: Formulation and evaluation. Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation, 18(3), 934–951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-022-09695-1
El-Shenawy, A. A., Mahmoud, R. A., Mahmoud, E. A., & Mohamed, M. S. (2021). Intranasal in situ gel of apixaban-loaded nanoethosomes: Preparation, optimization, and in vivo evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech, 22(4), 147. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-021-02020-y
Garg, V., Singh, H., Bimbrawh, S., Kumar Singh, S., Gulati, M., Vaidya, Y., & Kaur, P. (2017). Ethosomes and transfersomes: Principles, perspectives, and practices. Current Drug Delivery, 14(5), 613–633. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201813666160520114436
Gawarkar-Patil, P., Mahajan, B., Pawar, A., & Dhapte-Pawar, V. (2024). Cubosomes: Evolving platform for intranasal drug delivery of neurotherapeutics. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 10(1), 91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-024-00665-7
Ghori, M. U., Mahdi, M. H., Smith, A. M., & Conway, B. R. (2015). Nasal drug delivery systems: An overview. American Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 3(5), 110–119. https://doi: 10.12691/ajps-3-5-2
Gizurarson, S. (1993). The relevance of nasal physiology to the design of drug absorption studies. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 11(3), 329–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-409X(93)90015-V
Goindi, S., Dhatt, B., & Kaur, A. (2014). Ethosomes-based topical delivery system of antihistaminic drug for treatment of skin allergies. Journal of Microencapsulation, 31(7), 716–724. https://doi.org/10.3109/02652048.2014.918667
Hamzah, M. L., & Kassab, H. J. (2024). Formulation and characterization of intranasal drug delivery of frovatriptan-loaded binary ethosomes gel for brain targeting. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications, 17, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.2147/NSA.S442951
Illum, L. (2000). Transport of drugs from the nasal cavity to the central nervous system. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 11(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-0987(00)00087-7
Jones, N. (2001). The nose and paranasal sinuses: Physiology and anatomy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 51(1–3), 5–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00172-7
Kozlovskaya, L., Abou-Kaoud, M., & Stepensky, D. (2014). Quantitative analysis of drug delivery to the brain via nasal route. Journal of Controlled Release, 189, 133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.06.053
Lane, A. P. (2004). Nasal anatomy and physiology. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics, 12(4), 387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2004.04.001
Misra, A., & Kher, G. (2012). Drug delivery systems from nose to brain. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 13(12), 2355–2379. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920112803341752
Mygind, N., & Dahl, R. (1998). Anatomy, physiology, and function of the nasal cavities in health and disease. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 29(1–2), 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(97)00058-6
Nainwal, N., Jawla, S., Singh, R., & Saharan, V. A. (2019). Transdermal applications of ethosomes–a detailed review. Journal of Liposome Research, 29(2), 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1080/08982104.2018.1517160
Nerella, N., & Vasudha, B. (2024). Design, development, and optimization of sumatriptan loaded ethosomal intra-nasal nanogel for brain targeting. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Research, 12(4), 83–98. https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v12i4.610
Pakhale, N. V., Gondkar, S. B., & Saudagar, R. B. (2019). Ethosomes: Transdermal drug delivery system. Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics, 9(3), 729–733. https://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v9i3.2692
Pires, P. C., Paiva-Santos, A. C., & Veiga, F. (2023). Liposome-derived nanosystems for the treatment of behavioral and neurodegenerative diseases: The promise of niosomes, transfersomes, and ethosomes for increased brain drug bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals, 16(10), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101424
Raghuvanshi, A., Shah, K., & Dewangan, H. K. (2022). Ethosome as antigen delivery carrier: Optimisation, evaluation, and induction of immunological response via nasal route against hepatitis B. Journal of Microencapsulation, 39(4), 352–363. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652048.2022.2084169
Rattanapak, T., Young, K., Rades, T., & Hook, S. (2012). Comparative study of liposomes, transfersomes, ethosomes and cubosomes for transcutaneous immunisation: Characterisation and in vitro skin penetration. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 64(11), 1560–1569. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01535.x
Shelke, S., Shahi, S., Jadhav, K., Dhamecha, D., Tiwari, R., & Patil, H. (2016). Thermoreversible nanoethosomal gel for the intranasal delivery of eletriptan hydrobromide. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 27(6), 103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-016-5713-6
Tiwari, S. B., & Amiji, M. M. (2006). A review of nanocarrier-based CNS delivery systems. Current Drug Delivery, 3(2), 219–232. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720106776359230
Verma, P., & Pathak, K. (2010). Therapeutic and cosmeceutical potential of ethosomes: An overview. Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research, 1(3), 274–282. https://doi.org/10.4103/0110-5558.72415
Vyas, T. K., Shahiwala, A., Marathe, S., & Misra, A. (2005). Intranasal drug delivery for brain targeting. Current Drug Delivery, 2(2), 165–175. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201053586047