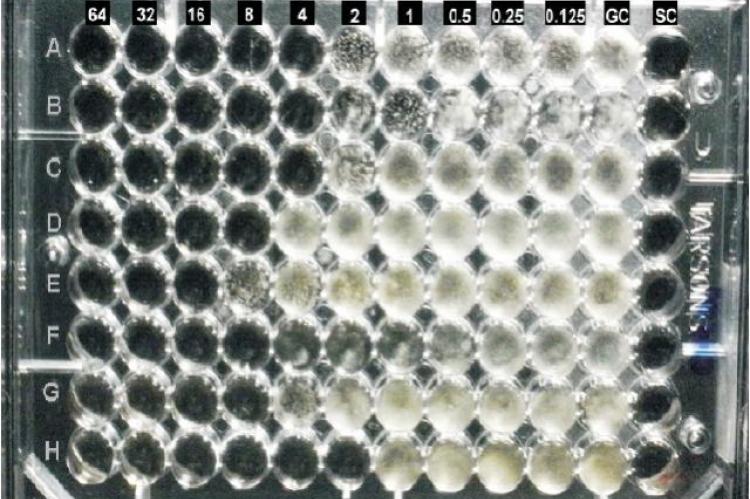
The antifungal activities of most commonly used biocide chlorhexidine gluconate tested against eight pharmaceutical clean room fungal isolates like Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus terreus, Penicillium sp., Curvularia sp., Cladosporium sp., and Alternaria sp. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) determined by using micro broth dilution method as per clinical and laboratory standards institute (CLSI) guidelines. No data exists on the determination of MIC of chlorhexidine gluconate on pharmaceutical clean room fungal isolates. MIC of chlorhexidine gluconate against species of Aspergillus and Penicillium species were ranged between 4 and 16 µg/mL. MIC of Curvularia, Cladosporium and Alternaria species also showed less than 8 µg/mL. This is the first study report using the CLSI broth microdilution antifungal susceptibility testing to determine the MIC value of chlorhexidine gluconate.
View:
- PDF (1.43 MB)