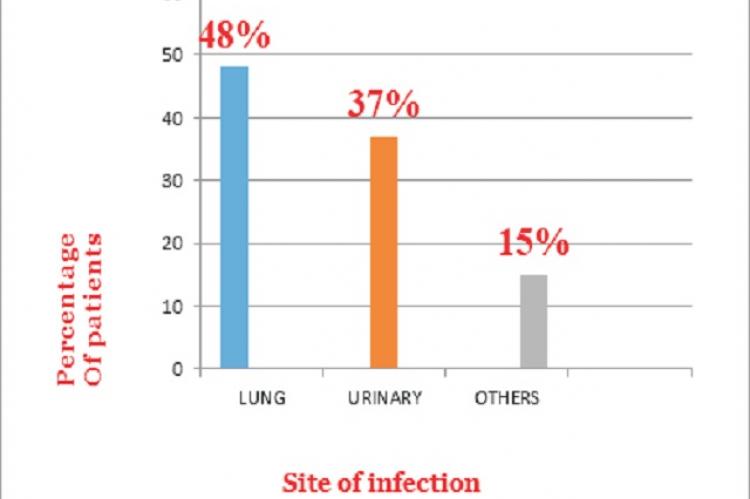
Sepsis is defined as a life threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to an infection. When people suffer from sepsis, it results in widespread inflammation, swelling and blood clotting. This study targeted to assess the management and treatment outcome of sepsis. The study aims to identify the treatment patterns followed in various departments of hospital, to provide counseling to patients/bystanders, to give awareness to nursing professionals for early identification of sepsis. The study is a prospective observational study conducted for a period of one year. Patients and their caregivers were educated for special care on sepsis. An awareness session was provided to nursing professionals on early identification and care on sepsis. A total of 115 patients were recruited for the study that was screened for sepsis by Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome criteria. The result of the study indicated that there is a higher prevalence of sepsis patients with pulmonary disorders. Majority (63%) of the patients were provided with cephalosporins to treat the infection. 85% of the patients had a past history of diseases. Counseling was provided during ward rounds to patients and bystanders. 95% of the patients have recovered from the disease condition.The primary treatment provided, the details of the patients who were subjected to culture studies, treatment provided during discharge, patient counseling and educational programs to nurses were done during the study.
View:
- PDF (234.38 KB)