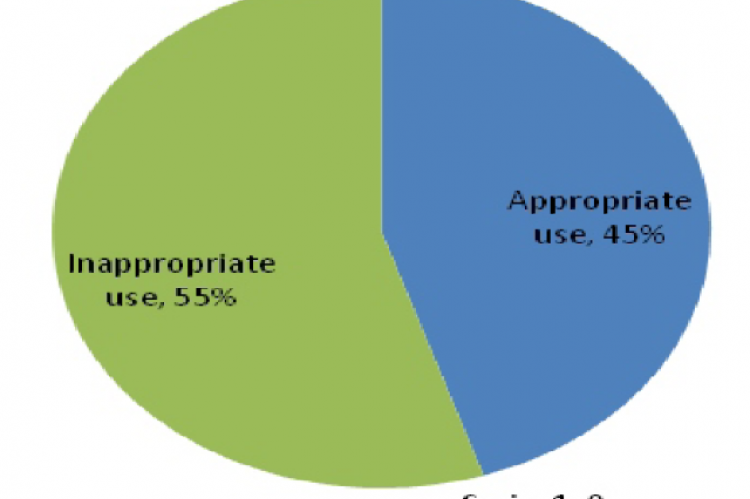
Inappropriate use of antibiotics can produce harmful effects on the society as well on the individuals. Self-medication with antibiotics leads to antibiotic resistance and many other health hazards. Antibiotic resistance is rising to dangerously high levels in all parts of the world and inappropriate use is identified as the key reason. Hence, a descriptive study was conducted using self-administered questionnaire among 400 conveniently selected students from different colleges in Asir region. The questionnaire contained 23 questions about the socio-demographic background and prevalence of antibiotic use. To assess the level of inappropriate use of antibiotics, six key questions were selected and scores were given to each respondent based on their response for these questions. The total score was calculated and categorized under proper use (score 4-6) or improper use (score 0-3). Data was analysed using SPSS version 23 and Chi square test was applied to determine the significance. The research revealed that more than half of the sample used antibiotics for various illnesses. The illness for which antibiotic was used the most was sore throat. It was also observed that more than two third of the sample had used antibiotics without prescription and nearly half of the sample had used antibiotics for 3 days or less. More than one quarter of sample had used OTC antibiotic many times in the previous year. The study revealed alarmingly high percentage of university students, inappropriately using antibiotics. High prevalence of inappropriate use was observed among the students who were enrolled in health sciences.
View:
- PDF (4.65 MB)