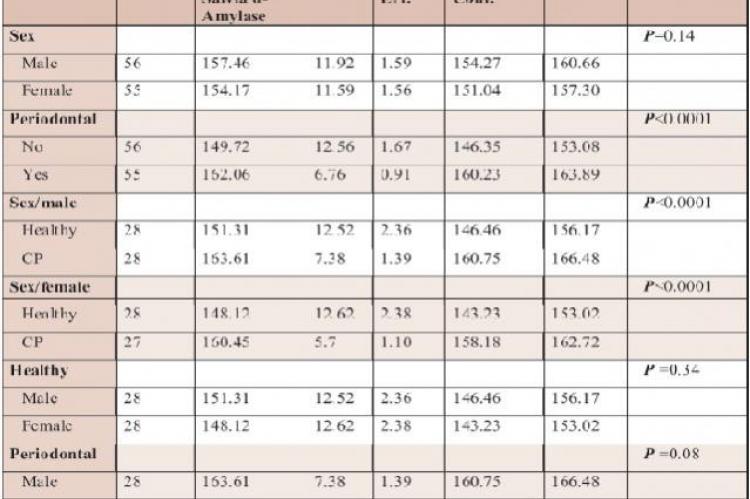
The composition of whole salivary proteins can be changed in many diseases, such as periodontal disease, compare to healthy people. In fact, host response against periodontal microbial causes these changes in profile of salivary proteins.This study investigated the relation between level of salivary and serum alpha- amylase (AA) and chronic periodontitis (CPIn this casecontrol investigation, un-stimulated whole saliva and serum sample was collected from 111 patients between 30-60 years old (including 55 females and 56 males). They were divided intofour groups: CPfemales, Healthy females (controls), CP males and Healthy males considering age and gender match (p> 0.05). Mean levels of salivary and serum AA was assayed by spectrophotometric method to assay enzyme kinetics. Data were analyzed using student's t-test and chi-square test. Salivary AA was significantly higher in CP group compare to control group (P<0.0001). Serum AA was not statistically significant in CP group as compared to healthy control group (P=0.07). In healthy group mean salivary AA levels were not statistically significant in males than females (P=0.34). Asignificant association was noticed between salivary AA and CP. However, there was not significant association between serums AA with CP. More research to demonstrate the real relation between AA and CP is recommended.
View:
- PDF (506.01 KB)