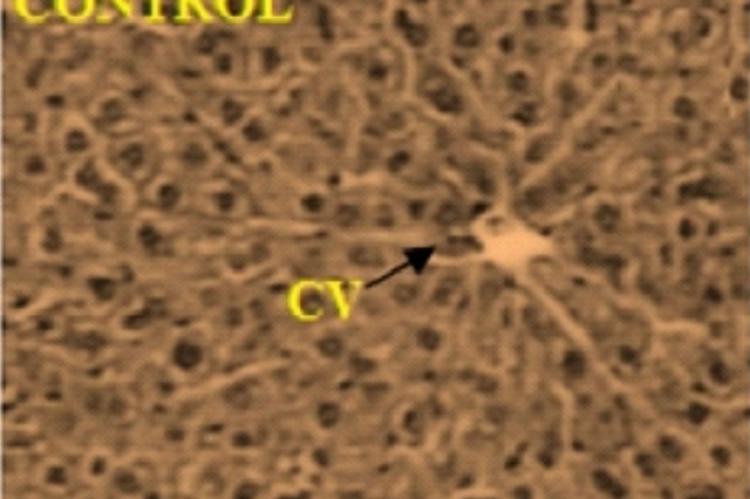
The present study was designed to evaluate hepatoprotective potential of the ethanolic fruit extract of Solanum xanthocarpum against D-galactosamine-induced hepatopathy induced liver toxicity in experimental animals. In the present study, in- vivo hepatoprotective effect of 50% Ethanolic fruit extract of Solanum xanthocarpum (SXE, 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight) was evaluated using two experimental models Dgalactosamine (D-GalN) (200 mg/kg, body weight, i.p.) induced hepatotoxicity in experimental animals. The hepatoprotective activity was assessed using various biochemical parameters like aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatise (ALP), γ-glutamyl transferase (γGT) and total bilirubin. Meanwhile, in vivo antioxidant activities as lipid peroxidation (LPO), reduced glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) were screened along with histopathological studies. Obtained results demonstrated that the treatment with SXE significantly (P<0.05- P<0.001) and dose-dependently prevented chemically induced increase in serum levels of hepatic enzymes. Furthermore, SXE significantly (up to P<0.001) reduced the lipid peroxidation in the liver tissue and restored activities of defence antioxidant enzymes GSH, SOD and catalase towards normal levels. Histopathology of the liver tissue showed that SXE attenuated the hepatocellular necrosis and lead to reduction of inflammatory cells infiltration. The results of this study strongly indicate the protective effect of SXE against acute liver injury which may be attributed to its hepatoprotective activity, and there by scientifically support its traditional use.
View:
- PDF (674.37 KB)