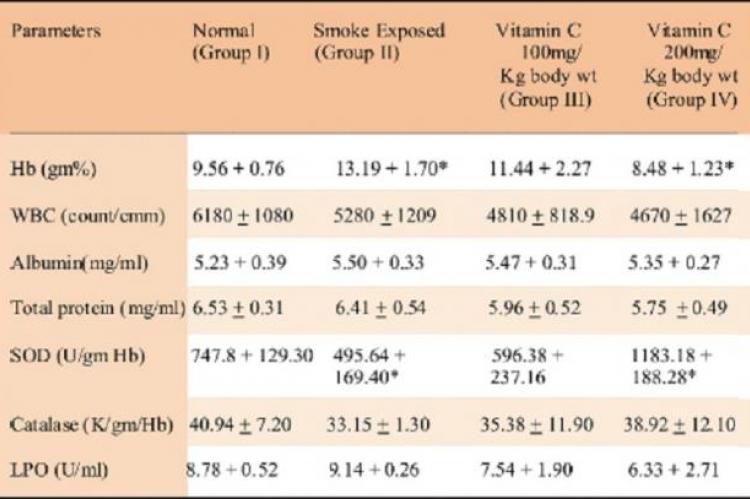
Male wistar rats were exposed to cigarette smoke along with supplementation of vitamin C at two doses (100mg and 200mg/kg body wt) for a period of one month. At the end of the experiment the rats were sacrificed and blood and lung tissues were collected for evaluation of antioxidant status. The depleted levels of antioxidant enzymes like SOD and Catalase were found to be elevated after treatment with vitamin C (200mg/kg body wt) (p<0.005). The smoke exposure was also found to increase the values of lipid peroxidation, hydroperoxides and conjugated dienes. Elevated values of all these were found to become normal with the treatment of vitamin C at a dose of 200mg/kg body wt, indicating the short term beneficial effect of vitamin C as a free radical scavenger against cigarette smoke.
View:
- PDF (610.04 KB)