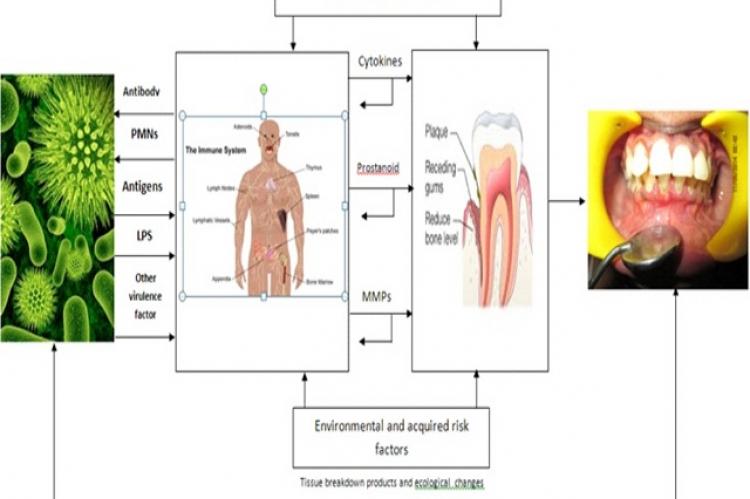
Periodontitis is one of the most prevalent chronic inflammatory diseases in humans. Periodontitis is chronic infectious condition of supporting tissues of teeth caused by sub gingival microbial colonization in susceptible hosts. Current understanding of the periodontal pathogenesis emphasizes the role of host response to pathogens in periodontal destruction. Immune inflammatory response of the host is a double edged sword which is protective by intent paradoxically resulting in tissue destruction. In periodontal disease, typical antimicrobial intervention procedures, such as scaling and root planning (SRP), will help in removing etiologic agents associated with inflammation, thereby helping to arrest periodontitis. However, such procedures do not inhibit the host mediated tissue destruction and do not offer necessary resolution of inflammation to restore tissue homeostasis. Host-modulatory pharmacotherapies are specifically target the host response mechanisms and such therapies as an adjunct to traditional antimicrobial interventions represents a new integrated approach in the management of periodontal disease. This review will cover an update on past and future host immune modulatory agents used adjunctively to treat and manage periodontal diseases.
View:
- PDF (238.38 KB)