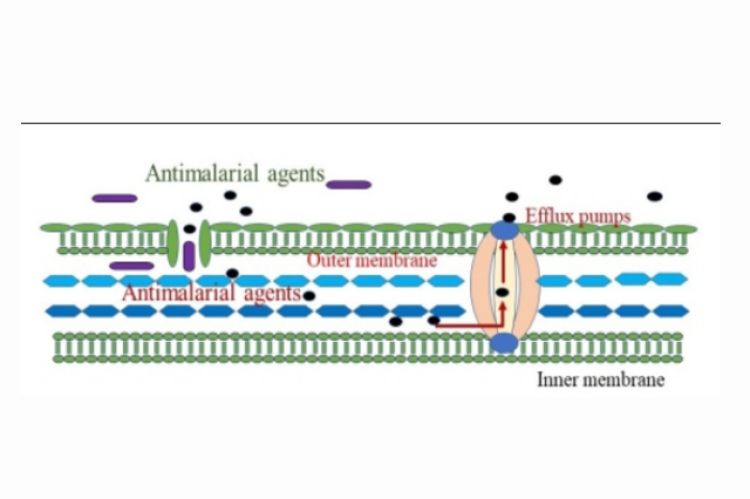
Malaria is generally controlled through pharmacological therapy and is preventable to a certain extent. Most antimalarial drugs that have been in use for decades are now limited owing to the emergence and spread of drug resistance. Mechanisms of antimalarial activity and drug resistance: Indian antimalarial medicinal plants. A thorough search for antimalarial drugs was conducted in several databases, including Scopus, Embase, Cochrane, and PubMed. The keywords used for the search were antimalarial drugs, mechanisms of action, antimalarial resistance, and Indian medicinal plants. This study included all publications in English. Studying the method of action of drugs and the mechanism of drug susceptibility is critical for optimizing their benefits and developing novel therapies with new targets. Little is known about the function of antimalarial medications and development of resistance. Many chemicals used for antimalarial activity have developed resistance. The demand for new antimalarial medicines has prompted significant efforts to develop novel antimalarial drugs from plants. Information from different Indian tribal communities and research publications was collected and compiled. The mechanisms of action, drug resistance, and antimalarial agents of Indian medicinal herbs have been documented in this study. This would aid future research on the antimalarial activity in plants.
View:
- PDF (804.8 KB)