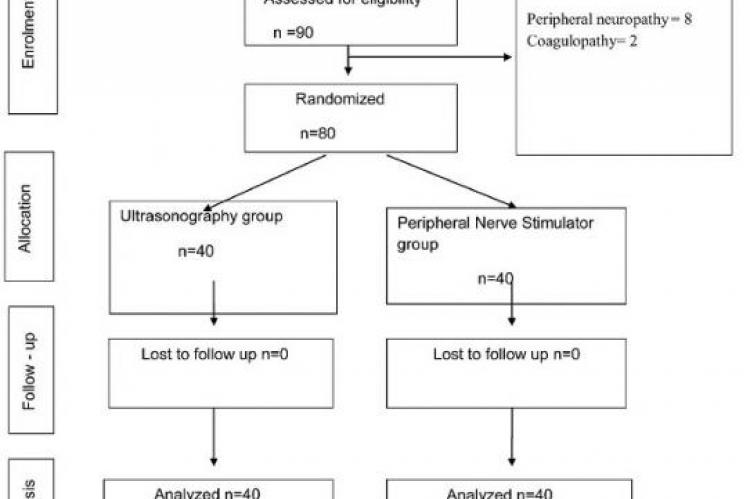
Introduction: Supraclavicular brachial plexus (SCBP) block provides effective regional anaesthesia to upper extremity. SCBP block can be performed by peripheral nerve stimulator (PNS) guided or ultrasound (USG) guided technique. An attempt was made in the present study to compare efficacy of SCBP block administered by using USG guidance Vs. PNS guidance. Methods: Eighty patients scheduled for elective upper limb surgery were randomly divided into two groups. Group USG, and Group PNS received ultrasound guided and peripheral nerve stimulator SCBP block respectively using Inj. bupivacaine. Primary outcome measures were success rate, onset and duration of sensory neural blockade, and need for supplementation of analgesia. Secondary outcome measure was complications. Comparison of quantitative and qualitative variables was done using unpaired student’s “t” test and chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test respectively. Results: Success rate was significantly higher in USG group (90.0 %) than PNS group (72.5 %). Mean time taken to give block was significantly longer in USG (15.6 minutes) than PNS (10.0 minutes) technique. Mean onset of sensory blockade was significantly earlier in USG (9.2 minutes) than PNS (10.6 minutes) group. Percentage of patients who required supplementary analgesia was significantly higher in PNS (27.5 %) than USG group (10.0 %). Four (10.0 %) and 11 (27.5 %) patients required conversion to general anaesthesia in USG group and PNS group respectively (p=0.001). Conclusion: USG guided SCBP block has high success rate, quick onset of sensory block, less requirement of supplementary analgesia, and less conversion to general anaesthesia as compared to PNS group.
View:
- PDF (7.59 MB)