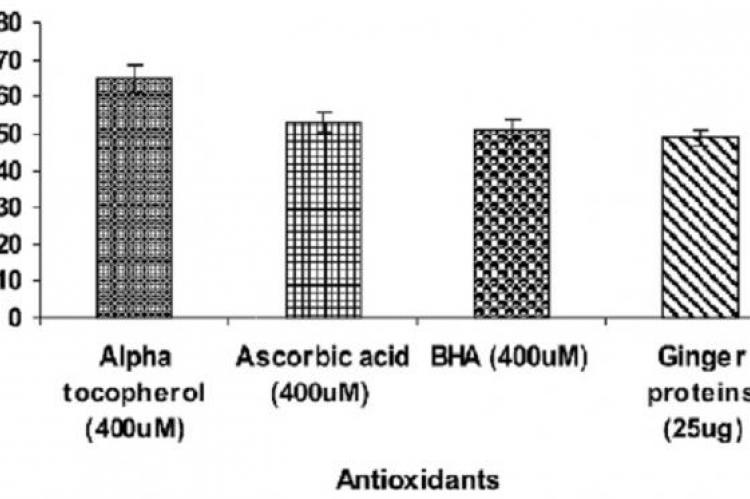
The study was done to investigate the in vitro antidiabetic activity of proteins from Ginger tuber. Phytochemicals of Ginger tuber proteins was analyzed by using standard methods. In vitro antioxidant studies were carried out for the Ginger tuber proteins using DPPH model, In vitro anti-diabetic studies was done by alpha amylase enzyme, alpha glucosidases enzyme inhibition studies and Glucose uptake in Yeast cells studies. The phytochemical screening of Ginger tuber proteins showed that the extract contains more proteins and contains negligible amount of other phytochemicals. The in vitro antidiabetic potential of extract was confirmed through alpha amylase enzyme, alpha glucosidases enzyme inhibition studies and Glucose uptake in Yeast cells studies. The results of the present study concluded that the Ginger tuber proteins possess significant antioxidant and antidiabetic activity. The potential pharmacological activity of Ginger tuber proteins might be due to the presence of proteins
View:
- PDF (797 KB)