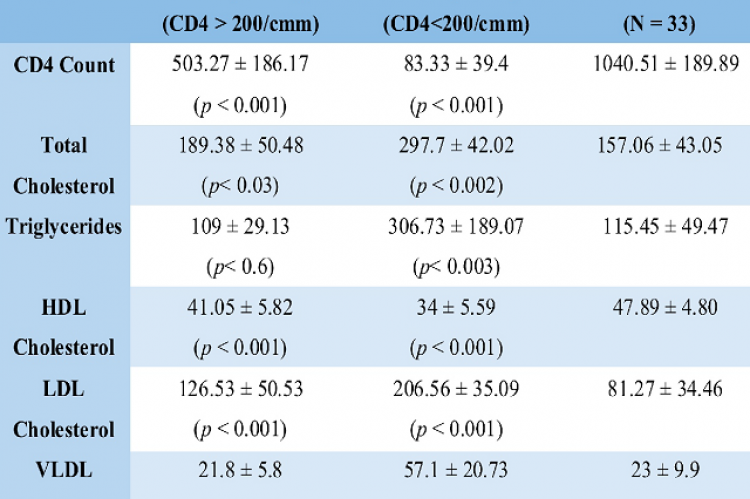
To assess the lipid profile in HIV and TB co-infected patients receiving drugs and to correlate any variations between the lipid parameters and the CD4 cell counts and to establish relationship between the variables. Fasting blood samples were collected from 33 HIV and TB co-infected patients on combined anti-tubercular and anti-retroviral therapy and 33 healthy controls. Lipid profiles were analysed by enzymatic kit methods and CD4 count were estimated in flow cytometer (BDFACS). Statistical analysis was done by statcalc software. High mean Serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL and VLDL cholesterol, and low HDL cholesterol levels were seen among patients with CD4 cells less than 200/ cmm. Whereas high mean serum total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol and normal triglyceride levels were seen in comparison to control in patients with CD4 cell count more than 200 cells/ cmm. Neither any correlation was established between CD4 cell count and lipid parameters nor between lipid parameters and duration of drug therapy. Severe dyslipidemia is an associated complication in later stage of HIV-TB co-infected patients on combined therapy. Multiple host factors as well as anti-retroviral drugs precipitate dyslipidemia. In early stage of the disease serum triglycerides and VLDL cholesterol levels remain normal. Follow up of the patients should be undertaken for dyslipidemia related complications in all HIV-TB co-infected patients irrespective of their stages.
View:
- PDF (831.16 KB)