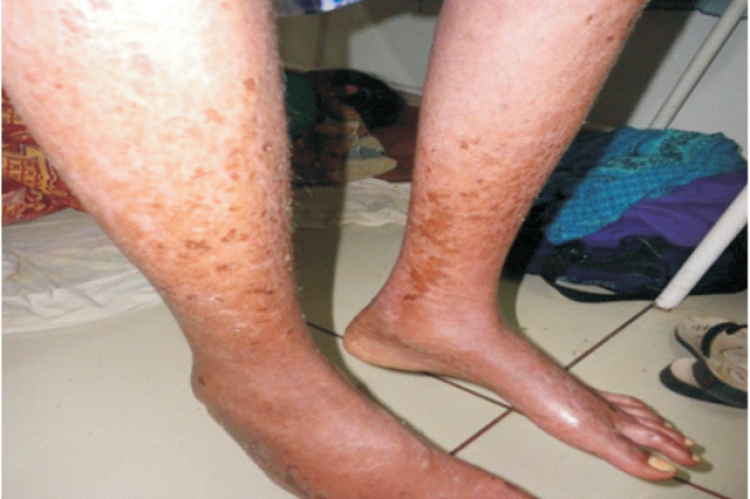
Tuberculosis (TB) is a common infectious disease in the developing countries and first line anti-tubercular drugs are found to be effective. Exfoliative dermatitis caused by ethambutol is an uncommon, but serious adverse drug reaction. After one month of anti-tubercular therapy, a patient developed papulovesicular skin lesions of bilateral limbs and dechallenge was done. The condition worsened and she was treated with IV hydroxyzine 25mg, IV pheniramine maleate SOS, Oint. Betamethasone as topical steroid and liquid paraffin for the management of exfoliate dermatitis. On rechallenge, it was found that ethambul was found be reason for the dermatitis and was discontinued. Early recognition of the reaction and cessation of the causative drug can stop the progression of skin rashes and normalize the patient as in this case.
View:
- PDF (3.15 MB)