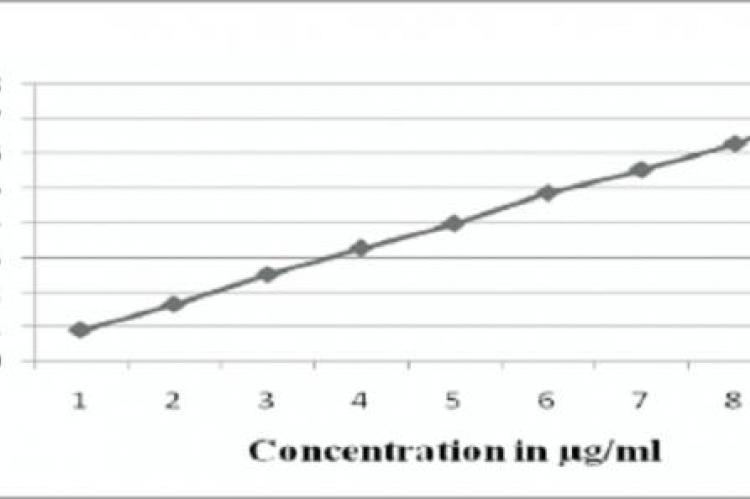
Concentrated aqueous hydrotropic solutions of sodium benzoate, sodium salicylate, urea, nicotinamide, sodium citrate and sodium acetate have been observed to enhance the aqueous solubilities of many poorly water-soluble drugs. Hydrotropic solubilization involves the addition of large amount of a second solute to increase the aqueous solubility of the first solute and precludes the use of organic solvents. These hydrotropes are economic and pollution-free. In the present investigation, 1.5M Urea solution was employed as hydrotropic solubilizing agent to solubilize poorly water-soluble drug Rosuvastatin for its spectrophotometric analysis. Rosuvastatin exhibits absorption maximum at 238nm .Beer’s law was found to be obeyed in the concentration range of 2-10μg/mL. In this method, there is no interference from any common pharmaceutical additives and diluents. The correlation co-efficient (' r ' value) for Rosuvastatin was0.99955.The results of analysis have been validated as per ICH guidelines. The percentage recoveries obtained for Rosuvastatin Calcium ranges from 99.93 to 99.97 %. The method is accurate, precise and economical.
View:
- PDF (816 KB)