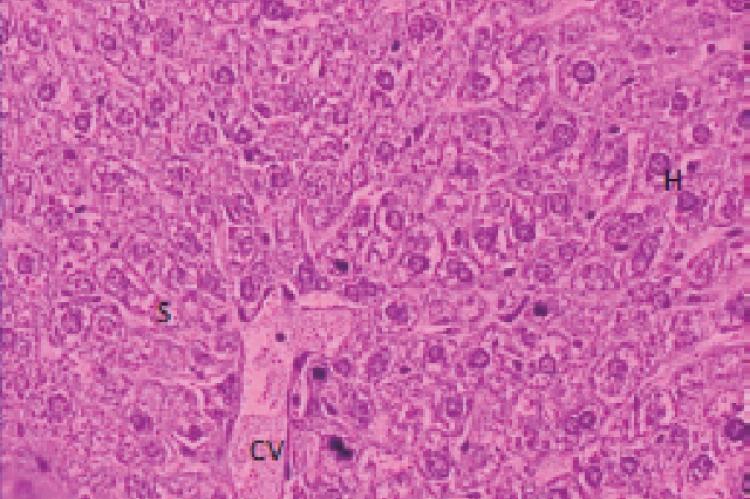
Aflatoxin, a class of mycotoxins produced by fungal spices of genus Aspergillus are contaminants of feed ingredients routinely used for poultry rations. This is considered to be one of the most potent hepatotoxin and a well known hepatocarcinogen. Hence the present aim of the study is to elucidate hepatoprotective potential of Curcuma longa and Curcumin on aflatoxin B induced histobiochemical alterations in Swiss albino mice. Toxicity was developed by oral administration of AFB1 at a dose of (2 5g/kg body wt) for 45 days in male mice. Curcuma longa (100 and 200 mg/kg body weight) and Curcumin (50 and 100 mg/kg body wt.) was given simultaneously for 45 days. The enhanced level of tissue lipid peroxide in AFB1 treated mice was accompanied by decrease in the levels of reduced glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and catalase. Administration of Curcuma longa and Curcumin lowered the level of lipid peroxidation and enhanced the antioxidant status of animal. Histological examination of the liver revealed pathophysiological changes in aflatoxin group and treatment with Curcuma longa and Curcumin improved liver histology. Our results suggest that Turmeric rhizome powder (Curcuma longa) and Curcumin showed protective effects against AFB induced toxicity by modulating lipid peroxidation and augmenting antioxidant defense system
View:
- PDF (1.74 MB)